Flowering plants, also known as angiosperms, are a diverse and vital group of plants that produce flowers and seeds. They encompass a vast range of species, from familiar garden blooms to towering trees, and they play a crucial role in ecosystems and human life https://mojdomowyazyl.pl. In this article, we will explore the unique characteristics of flowering plants, their ecological importance, their uses in various fields, and some interesting facts about them.
Characteristics of Flowering Plants
Flowering plants are distinguished by their ability to produce flowers, which are reproductive structures designed to facilitate pollination and seed production. Key characteristics include:
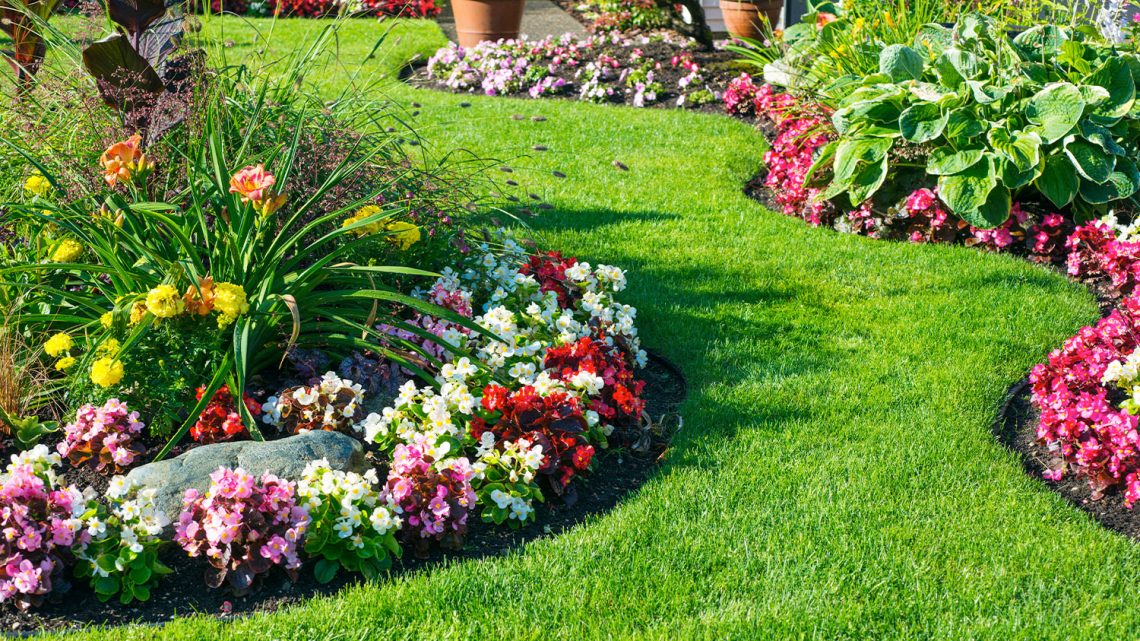
- Flowers: The most notable feature, flowers come in various shapes, sizes, and colors, attracting pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds. A flower typically consists of four main parts: sepals, petals, stamens (male reproductive organs), and carpels (female reproductive organs).
- Seeds and Fruits: After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed, while the ovary matures into a fruit, which protects the seeds and aids in their dispersal. Fruits can be fleshy, like apples and cherries, or dry, like nuts and grains.
- Vascular System: Flowering plants have a complex vascular system made up of xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, while phloem distributes sugars and nutrients throughout the plant.
- Diversity: Angiosperms are the most diverse group of plants, with over 300,000 known species. They inhabit various environments, from tropical rainforests to arid deserts, adapting to their surroundings in remarkable ways.
Ecological Importance
Flowering plants are essential to ecosystems for several reasons:
- Pollination and Food Production: Many flowering plants rely on pollinators for reproduction. This symbiotic relationship not only ensures the survival of plant species but also provides food for various animals, including humans. Crops like fruits, vegetables, and grains depend on flowering plants for their existence.
- Habitat and Shelter: Flowering plants provide habitats for countless species of insects, birds, and mammals. Trees, shrubs, and herbaceous plants create layers of habitat that support diverse wildlife.
- Soil Health: The root systems of flowering plants help stabilize soil, preventing erosion and maintaining soil health. Additionally, they contribute organic matter to the soil through leaf litter and decaying plant material, enhancing nutrient availability.
- Climate Regulation: Plants, including flowering species, play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Human Uses of Flowering Plants
Flowering plants have been integral to human culture and civilization for centuries. Their uses are manifold:
- Agriculture: Many flowering plants are cultivated for food, such as grains (wheat, rice), fruits (apples, oranges), and vegetables (carrots, lettuce). The agricultural industry heavily relies on flowering plants for sustenance.
- Medicinal Uses: Numerous flowering plants have medicinal properties and are used in traditional and modern medicine. For example, plants like echinacea and lavender have therapeutic benefits, while others are sources of vital pharmaceuticals.
- Aesthetic Value: Flowering plants are celebrated for their beauty and are widely used in landscaping and horticulture. Gardens, parks, and public spaces often feature a variety of flowering species to enhance visual appeal and promote biodiversity.
- Cultural Significance: Flowers hold symbolic meanings in many cultures. They are used in rituals, celebrations, and expressions of love and appreciation. For example, roses symbolize love, while chrysanthemums are associated with honor and respect.
Fascinating Facts About Flowering Plants
- Oldest Flowering Plant: The oldest known flowering plant, Archaefructus, dates back to about 125 million years ago, providing insight into the early evolution of angiosperms.
- Largest Flower: The Rafflesia arnoldii, found in Southeast Asia, produces the world’s largest single flower, measuring up to three feet in diameter and emitting a strong odor resembling decaying flesh to attract pollinators.
- Fastest Growing Plant: Bamboo, a flowering plant, can grow up to 35 inches in a single day under optimal conditions, making it one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth.
- Diverse Pollination Strategies: Flowering plants have evolved various strategies to attract pollinators, including vibrant colors, enticing scents, and even mimicking the appearance of female insects to lure males.